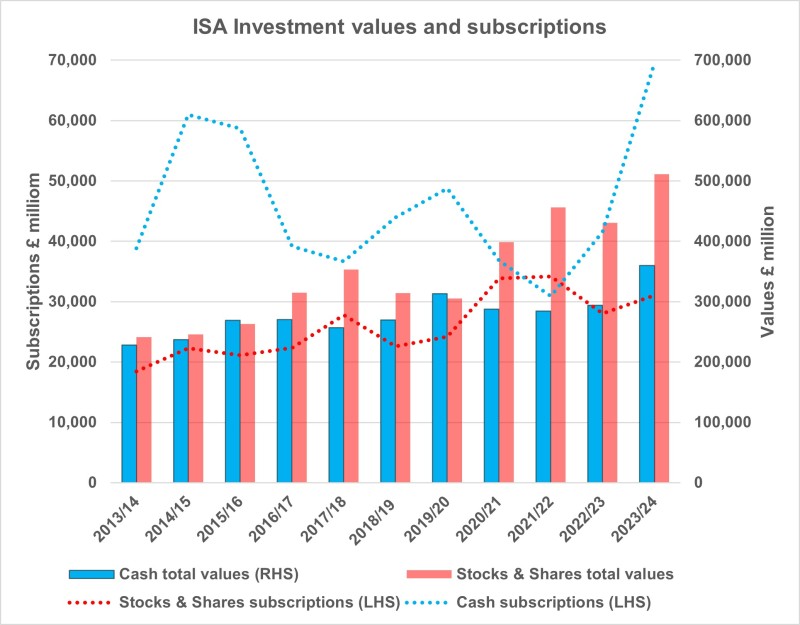
The HMRC figures for 2023–2024 show that subscriptions to cash ISAs have increased by nearly 224% more than stocks and shares ISAs in the decade since 2013–2014.
Source: HMRC.
However, with the 2025 Autumn Budget due at the end of November and ISAs on the Chancellor’s agenda, what does this mean for future savings and investments?
Will the HMRC ISA rules change?
For some time, Chancellor Rachel Reeves has been planning to reform Individual Savings Accounts. It’s widely believed that the current HMRC ISA allowance – the maximum limit of £20,000 per tax year – is going to be reduced for cash ISAs, despite disapproval from the big banks.
The recent statistics from HMRC cast new light on this debate. While stocks and shares ISA subscriptions totalled £31 billion in 2023–2024, cash ISA subscriptions amounted to £69.5 billion, bringing the decade’s total investment in cash ISAs to £360 billion by April 2024.
Assuming this total has now surpassed £400 billion, it would create £16 billion in interest that HMRC isn’t collecting tax on. To the Chancellor, lowering the savings cap on cash ISAs could help to reduce tax loss, as the most recent estimate suggests £9.4 billion was lost in 2024–2025 through untaxed ISAs.
This was up almost 20% from the previous year, after little net inflow for cash ISAs for most of the previous decade when the Bank of England rate was lower and provided worse returns.
It makes sense, then, that the Chancellor would feel justified in changing the rules for cash ISAs – but we will have to wait to see what is announced in the Autumn Budget.
Should you get a cash ISA right now?
Before you rush to set up a cash ISA before the Budget ushers in any changes, you should think carefully about what you want to achieve with your savings deposits.
If you only want to move money to a tax shelter, unless you’re an additional rate taxpayer, the Personal Savings Allowance already covers up to £200 of tax on personal interest.
Or, if you’re aiming to set money aside for long-term growth, there may be better options available.
More details on how ISAs work can be found on the government website, or you can speak to a financial adviser, like one of our Barnsley accountants, to help you explore a range of options.
At gbac, we offer a wide selection of financial services, so we would be happy to discuss tax planning and investment possibilities with you. Simply contact us to talk at a time that suits you.
When used wisely, company loans can be an effective way for directors to access company funds quickly. However, a company loan can also come with serious tax implications.
It’s important for directors to be aware of the ways that taking a company loan can affect their tax liability. Before taking this step, here’s what company directors should know.
Personal tax on director’s loans
Most directors will already know that a company loan could affect their personal tax if there are taxable benefits. If the loan interest is lower than the HMRC rate (3.75%) and the director’s beneficial loans total more than £10,000 during the same tax year, there will be a tax charge.
However, the beneficial loan tax charge isn’t that significant for directors paying the higher tax rate. For example, an interest-free loan of £20,000 for 6 months would only cost £150 in tax.
Company tax on director’s loans
If the individual is the director of a close company and a shareholder, the tax situation will become more complicated. The following rules generally apply to owner-managed companies:
- If a loan is repaid by the deadline for the company to pay Corporation Tax (9 months and 1 day from the end of their accounting period) then there will be no tax charge.
- If the loan isn’t repaid in full by then, there will be a company tax charge in addition to their Corporation Tax bill, applying 75% to the outstanding loan amount.
- The tax charge will be refunded back to the company if the director repays the loan.
This tax charge means that larger loans can become expensive for directors if they can’t repay. The loan will also be a red flag on the company’s balance sheet that may discourage investors or customers.
Get advice on director’s loan tax
If you are a director and borrow money from or pay money into your company, you must keep records of your director’s loan account and include these details on the balance sheet in your annual reports.
More information about director’s loans, and reporting and paying tax on them, is published on the government website. There is also the possibility of outsourcing your accounts management to an agent who can manage your financial records, filing, and taxes for you.
Here at gbac, our accountants in Barnsley can provide a range of services to help company directors with efficient financial management, from corporate finance to tax consultancy and more.
To discuss our accounting services, contact us to book a consultation with our team.
Despite government plans to tighten company reporting regulations at Companies House, the Chancellor recently announced intentions to ‘cut red tape’ for small to medium businesses.
The rules for filing company accounts due to take effect from 1st April 2027 include:
- Micro-entities and small companies must file profit and loss accounts
- Small companies need to file a director’s report
- All companies can no longer file abridged accounts
However, as per the statement from Chancellor Rachel Reeves, the government intends to reduce pointless form-filling so that thousands of businesses can save time and money on admin.
Here’s more information on what could be changed for company reporting in 2027.
Loosening company reporting requirements
According to the Chancellor, the requirement for all companies to file a director’s report at Companies House is going to be removed. However, some aspects of the director’s report will be included in other parts of the company’s financial statements instead.
Additionally, medium-sized private companies will no longer be required to produce a strategic report explaining their business strategy and performance as part of their annual accounts.
Of course, companies will welcome any lightening of their administrative burden, but there are also concerns that the Chancellor’s latest plans don’t go far enough.
Further increasing company size thresholds
Companies House already significantly increased company size thresholds from April 2025, but the Chancellor has announced that these thresholds will be increased again.
For a company to be categorized as a micro-entity or a small company, its turnover, balance sheet total, and number of employees must be below the following thresholds:
| Micro-entity | Small company | Medium company | |
| Turnover | £1 million | £15 million | £54 million |
| Balance sheet | £500,000 | £7.5 million | £27 million |
| Employees | 10 | 50 | 50 |
These current thresholds apply to accounting periods that began on or after 6th April 2025. If they are increased again, more businesses will qualify for benefits such as reduced reporting requirements for micro-entities and potential audit exemptions for small companies.
Get help with filing annual accounts
Not sure about the Companies House annual accounts filing requirements, or how the latest company reporting regulations affect your business? Guidance on Companies House annual requirements is available online, but you also have the option of utilising professional accounts management.
At gbac, our experienced accountants in Barnsley can assist companies of all sizes with financial management services, covering bookkeeping, tax consultancy, statutory filing, and more.
To discuss what our team can do for your business, call 01226 298 298 or email info@gbac.co.uk today.
With a new online service launched by HMRC, taxpayers who need to pay the High Income Child Benefit Charge (HICBC) can do so in real time, instead of registering for self-assessment.
The HICBC applies if a parent/guardian (or their partner) has received Child Benefit while earning more than £60,000 a year. The charge removes 1% of the benefit for every £200 over this threshold, which means that the benefit is reduced to nil once their annual income reaches £80,000.
Read on to learn more about the online service and how to sign up to pay directly through PAYE.
How to pay the HICBC via PAYE
If an employee has no other reason to submit a self-assessment tax return, such as declaring property income, then they should be able to pay the HICBC through PAYE.
You can sign up to pay the Child Benefit tax charge through PAYE on the government website, but you’ll need to provide your National Insurance number, photo ID, and income details. Once you have registered successfully, HMRC should update your tax code within 48 hours.
The deadline to register for the online service is the 31st of January following the tax year the HICBC is payable for. Anyone who is already registered for self-assessment must deregister first.
If you haven’t yet submitted a return for the 2024–2025 tax year, you can choose to settle your HICBC liability through PAYE during the 2025–2026 tax year instead. However, if you’re also liable for the HICBC in 2025–2026, this means HMRC will recover both amounts in the same year.
After the current tax year ends, HMRC will only collect the HICBC via PAYE during the relevant tax year.
Get help managing your HICBC liability
Signing up to pay this tax charge directly as an employee should be straightforward. That said, some cases can be more complicated if relationships with partners change during the tax year.
For parents/guardians earning between £60,000–£80,000 a year, it may seem easier to simply opt out of receiving Child Benefit. It’s important to still claim, even while opting out of payments, to receive National Insurance credits that contribute to the individual’s State Pension.
If you aren’t sure what to do, it can be helpful to seek tax planning advice from professionals, like the team here at gbac. Our accountants in Barnsley can help you optimise your tax-free allowances.
For more information, please give us a call on 01226 298 298 or send an email to info@gbac.co.uk.
In a few months, it will become mandatory for sole traders and landlords earning more than £50,000 a year to use Making Tax Digital (MTD) – unless they are eligible for an exemption.
HMRC will make exemptions for traders or landlords who are ‘digitally excluded’ – which means they can’t switch to the new digital platform due to their age, health condition or disability, lack of broadband access, or inability to use a computer because of religious reasons.
Wondering whether you can avoid the MTD requirements? Here’s how valid exemptions will work.
What counts as digital exclusion from MTD?
For HMRC to allow you to avoid using MTD software, you must meet at least one of the following criteria:
- No internet access – Your home or business must be in a location where you can’t access the internet, and there must not be a suitable alternative location with access.
- Age, health, or disability – You must prove that your age, health condition, or disability prevents you from using a computer, tablet, or smartphone to manage digital records.
- Religion – You must show that you are a practicing member of a religious society that doesn’t use computers, tablets, or smartphones for business or personal purposes.
There may be other reasons for digital exclusion, so HMRC will consider them on a case-by-case basis.
If you have already been granted an exemption from using MTD software for VAT returns, then you will also be exempt from MTD for Income Tax as long as your circumstances stay the same.
Who isn’t digitally excluded from MTD?
HMRC will not accept applications for MTD exemption if the only reason for applying is that:
- You previously only submitted paper tax returns
- You’re unfamiliar with digital accountancy software
- You only have a few digital records each tax year
It’s expected that switching to and using MTD software may require additional costs and extra time at first, so HMRC won’t consider these valid reasons for exemption, either.
You can find more information about applying for an exemption from MTD on the government website, but you should only submit an application if you have a valid reason for digital exclusion.
Do you need help with MTD accounting?
If you want to apply for a Making Tax Digital exemption, you can either apply yourself or get someone else to apply on your behalf using HMRC’s contact details for general enquiries.
Even if you are unable to set up or use MTD software yourself, an easy way to comply with HMRC is to hire an agent who can use the digital software to manage your records and file returns for you.
Here at gbac, we have a team of experienced Barnsley accountants who can handle your digital accounts for you, ensuring efficient tax management year-round.
For more information on how we can help, call us on 01226 298 298 or email info@gbac.co.uk.
HMRC has been running the Let Property Campaign for over 12 years to make sure landlords who earn income by letting out residential property pay the correct tax in the UK.
The campaign pulled in a record £107 million in 2024–2025, which was over 60% more than the previous year. However, the number of voluntary disclosures actually fell from 11,000 to below 8,000.
With larger amounts being paid, this highlights the risk of ignoring nudge letters from HMRC, as the more you owe in outstanding tax, the greater the interest and penalties will be.
Here are some common mistakes that landlords should avoid when paying tax on rental income.
Common mistakes by residential landlords
Some tax errors are caused by deliberate evasion, but it can be easy to misunderstand property letting rules and pay the wrong amount of tax by accident. Common situations include:
- Renting out an inherited property – If the landlord only lets a single property after inheriting it, they may not realise that they still need to declare the income from this to HMRC.
- Moving in with a partner and renting out the other property – If someone moves into their partner’s home and lets their previous property, even if the rent only covers the mortgage payments so there isn’t really any profit, only the interest will qualify for tax relief.
- Purchasing a property for a child in university – A parent might purchase a property for their child to live in rent-free while studying at university. However, if the child allows rent-paying friends to move in with them, this income must then be declared to HMRC.
Capital expenditure can also confuse landlords when declaring taxable income, as only like-for-like replacements are deductible expenses, while significant property upgrades are not.
Do you need to make a voluntary disclosure?
This HMRC campaign only applies to landlords of residential properties and doesn’t apply to companies or commercial properties. Voluntarily disclosing untaxed rental income will make penalties more lenient.
More information about the Let Property Campaign is available on the government website to help you understand whether you need to make a disclosure, how to do this, and how to pay HMRC.
In some cases, as letting platforms provide information directly to HMRC, the tax agency may send nudge letters to prompt landlords to double-check their rental income and tax liabilities.
Whether you’ve already received a letter from HMRC or you think you may have declared the wrong amount, whatever the reason, you can seek help from a professional tax adviser.
Here at gbac, we have a team of experienced accountants in Barnsley who can provide a range of tax planning and tax management services for residential landlords in the UK.
To learn more, call 01226 298 298, or email your details to info@gbac.co.uk and we’ll be in touch.
After a proposal by the Bank of England to cap stablecoin holdings for individuals at £10,000 or £20,000 received strong criticism, the Bank may be softening this stance.
A stablecoin is a cryptocurrency that maintains a stable value in relation to a specific asset, such as the US dollar. It’s believed by many that a restriction on stablecoin holdings would leave the UK falling behind the EU and US when it comes to regulating digital assets.
As the proposed maximum for businesses is £10 million, it may be a relief to those using stablecoins that the Bank of England seems to be backtracking on its stance against this form of cryptocurrency.
Here’s what businesses should know about stablecoin holdings under the current rules.
Why does the Bank of England want to cap stablecoins?
The majority of stablecoins are currently tied to US dollar-based products, with some worth up to $300 billion circulating. While they aren’t mainstream yet, they’re convenient for investors and those carrying out cross-border transactions.
Individuals can park funds using stablecoin while buying and selling more volatile assets or use stablecoins to pay for things while avoiding the extra costs associated with traditional methods, like credit cards.
The Bank of England is concerned about the future emergence of sterling-dominated stablecoins in retail and wholesale payment systems in the UK, so the Bank is aiming to set up a regulatory framework for a ‘real world’ multi-money system in advance, which should be finalised next year.
What about other cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin?
While stablecoins are becoming an alternative option, many businesses hold Bitcoin as an asset. This is because holding Bitcoin provides more diversification and can offer protection against inflation compared to treasury assets like cash and gilts, while also making the business seem more digitally savvy.
However, Bitcoin holdings still come with risks, including price volatility and custodial challenges. These involve including Bitcoin on balance sheets at cost, as it’s classified as an intangible fixed asset under UK Generally Accepted Accounting Practice.
It’s also worth noting that crypto assets are treated like shares when it comes to Capital Gains Tax liability.
Need accounting advice on crypto holdings?
While it hasn’t been updated for a couple of years, the Bank of England has published a stablecoin guide that explains what they are, how they work, and the Bank’s current stance on their use in the UK.
If you need professional financial guidance on crypto assets and transactions, whether as an individual or as a business, you may want to consult financial advisers like our accountants in Barnsley.
Here at gbac, our experienced team can help you with accounting and tax management for traditional and digital currencies. Simply call us on 01226 298 298 or email info@gbac.co.uk to find out more.
As announced earlier this year, Companies House will be introducing mandatory identity verification this autumn. This process will be compulsory from 18th November 2025.
Depending on when their company’s next confirmation statement is due to be filed at Companies House, the date for directors to confirm they have verified their identity may vary.
Here’s what directors and persons with significant control (PSCs) will need to do from November 2025.
Verification for directors
All existing company directors must verify their identity with Companies House, but those who are directors of multiple companies will only need to register once.
Once a director’s identity has been verified, Companies House will send them an 11-character code. They must use this code the first time they file a confirmation statement for their company from 18th November.
If a confirmation statement is already due in early November, then the director won’t need to verify their identity until November 2026, so it may be worth filing early to defer verification.
All directors who are appointed on or after 18th November will need a personal code to proceed.
While the same identity verification requirements apply to members of limited liability partnerships (LLPs), identity verification will not be required for corporate directors until a later date.
Verification for PSCs
Like directors, people with significant control must also verify who they are. If you are both a director and PSC of the same company, you will need a separate personal code for each role, and you must submit the PSC code within 14 days of the company’s next confirmation statement date.
However, if you are a PSC but not a director, you must provide the code within 14 days of your birth month. For example, a PSC born in January must submit their code between the 1st and 14th of January 2026.
Anyone who becomes a PSC from 18th November 2025 onwards will need to provide their 11-character personal code within 14 days of registering at Companies House.
Get help with Companies House
More information about Companies House identity verification is available on the government website, but if you need professional assistance with filing company accounts, you can seek expert advice.
Here at gbac, we have a knowledgeable team of Barnsley accountants who can help businesses of all sizes comply with account filing requirements at Companies House.
For more information on how we can help you with company accounts, contact us by phone or email.
HMRC has now withdrawn the VAT652 form, which means companies that have made large errors in their VAT returns must follow updated processes to submit corrections.
Method 1 is required for smaller errors, while Method 2 is required for larger errors.
Here’s how to tell HMRC about an error on your VAT return from September 2025.
Method 1
The first method of correcting small errors on VAT returns simply lets taxpayers adjust their current tax return, which is allowed in the following scenarios:
The net error is less than £10,000(along with any previous errors in the last 4 years). For example, if you underpaid £11,000 on sales but underclaimed £2,000 on purchases, then the net error would be £9,000, so you could correct these errors using Method 1.
The net error is £10,000–£50,000 and less than 1% of the current return’s output. Meaning that for a £2.5 million output, you could correct a net error of up to £25,000 with Method 1.
Method 1 corrections will not receive late payment interest or penalties if the business has taken reasonable care to update their VAT return as soon as possible.
Method 2
Since the VAT652 form was withdrawn, any errors that are larger than the Method 1 allowances need to be corrected online (or otherwise by notifying HMRC in writing).
If your company needs to notify HMRC about a large VAT return error, you must include information about how it happened and when. Method 2 corrections will incur late payment interest charges.
Penalties for VAT return errors
If a business makes a VAT return error either deliberately or out of carelessness, then HMRC will apply VAT penalties for late payment. While you can still use Method 1 to correct careless errors, Method 2 must be used to correct deliberate errors.
To ensure you follow the right process, read HMRC’s guidance on how to amend VAT records.
If you find these processes confusing and want to make sure you avoid errors and penalties, you also have the option to consult financial experts like our accountants in Barnsley.
To enquire about help with VAT management, get in touch by calling 01226 298 298, or send an email to info@gbac.co.uk with your information and we’ll get back to you soon.